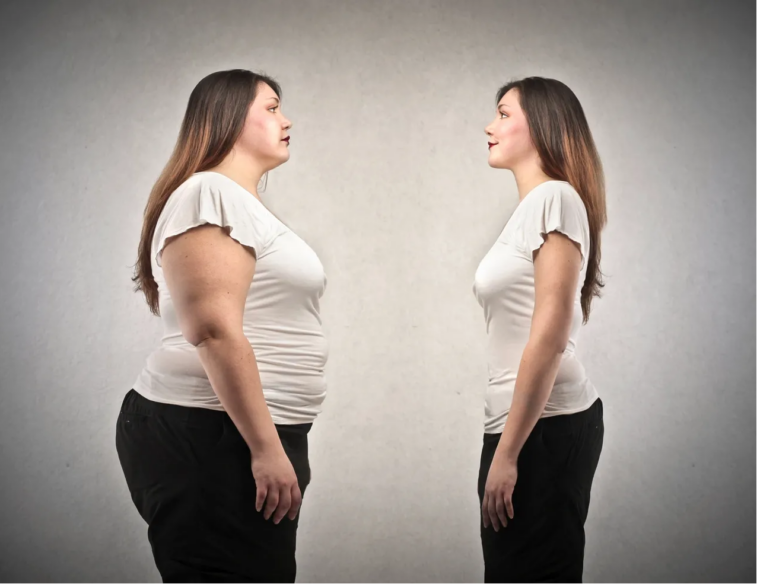
Today, let’s talk about one factor that affects our body: hypothyroidism. This condition occurs when the thyroid gland, which regulates metabolism, doesn’t function properly. It can lead to various symptoms, including weight gain and dry skin, so it’s important to understand it accurately. Let’s explore together!
Introduction to Hypothyroidism and Its Impact on Weight Gain
Hypothyroidism is a condition where the thyroid gland produces insufficient thyroid hormones, leading to a slowed metabolism. This can result in weight gain and various other symptoms. In this article, we will discuss the main symptoms of hypothyroidism, diagnostic methods, effective treatment options, and weight management strategies.
Main Symptoms and Diagnosis of Hypothyroidism
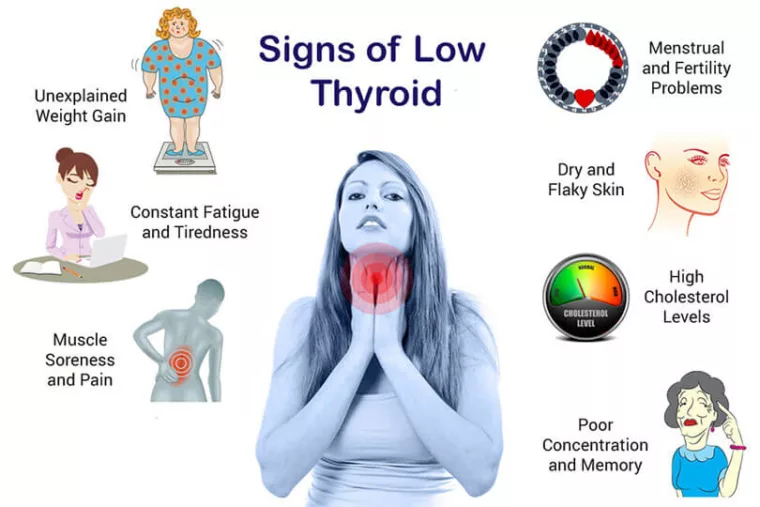
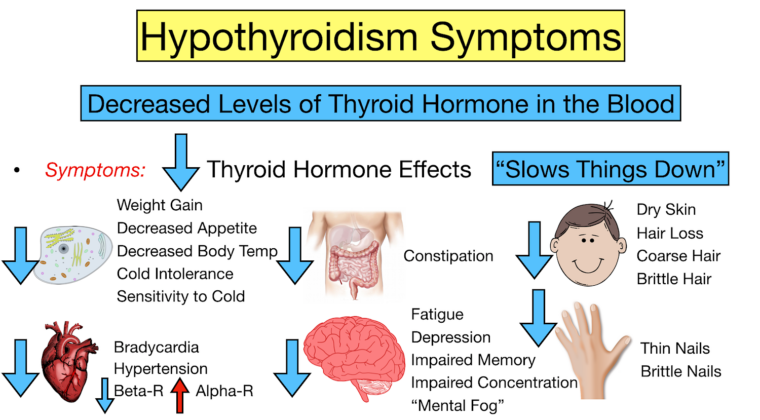
The main symptoms of hypothyroidism include:
- Weight Gain: A slowed metabolism due to hypothyroidism can lead to weight gain.
- Fatigue and Lethargy: A lack of thyroid hormones can decrease energy metabolism, causing fatigue and lethargy.
- Digestive Issues: Reduced activity of the digestive system can cause digestive problems.
- Skin Changes: Dry, itchy, and red skin may appear.
Hypothyroidism is diagnosed through blood tests. If the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels are high and the thyroid hormone levels (T3, T4) are low, it is likely hypothyroidism.
Understanding the Relationship Between the Thyroid and Weight Gain
The thyroid plays a crucial role in metabolism. Thyroid hormones regulate energy production within cells and stimulate metabolism. Therefore, a decrease in thyroid hormone secretion due to hypothyroidism can lead to a slowed metabolism and weight gain.
Factors That Make Weight Management Difficult
Hypothyroidism can make weight management challenging. The main factors include:
- Slowed Metabolism: A slowed metabolism due to hypothyroidism can easily lead to weight gain.
- Increased Appetite: Hypothyroidism can increase appetite, leading to higher food intake.
- Inability to Exercise: Fatigue and lethargy can make it difficult to exercise.
Necessary Tests for Diagnosing Hypothyroidism
To diagnose hypothyroidism, the following tests are needed:
- Blood Tests: Measure the levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and thyroid hormones (T3, T4).
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound can be performed to check the size and shape of the thyroid gland.
- Thyroid Function Tests: Detailed thyroid function tests can be conducted for a comprehensive evaluation.
Various Symptoms Beyond Weight Gain
Hypothyroidism can cause a range of symptoms beyond weight gain, such as:
- Headaches and Dizziness: Reduced blood circulation due to hypothyroidism can cause headaches and dizziness.
- Memory Loss: A lack of thyroid hormones can lead to memory loss.
- Depression: An imbalance in neurotransmitters due to a lack of thyroid hormones can cause depression.
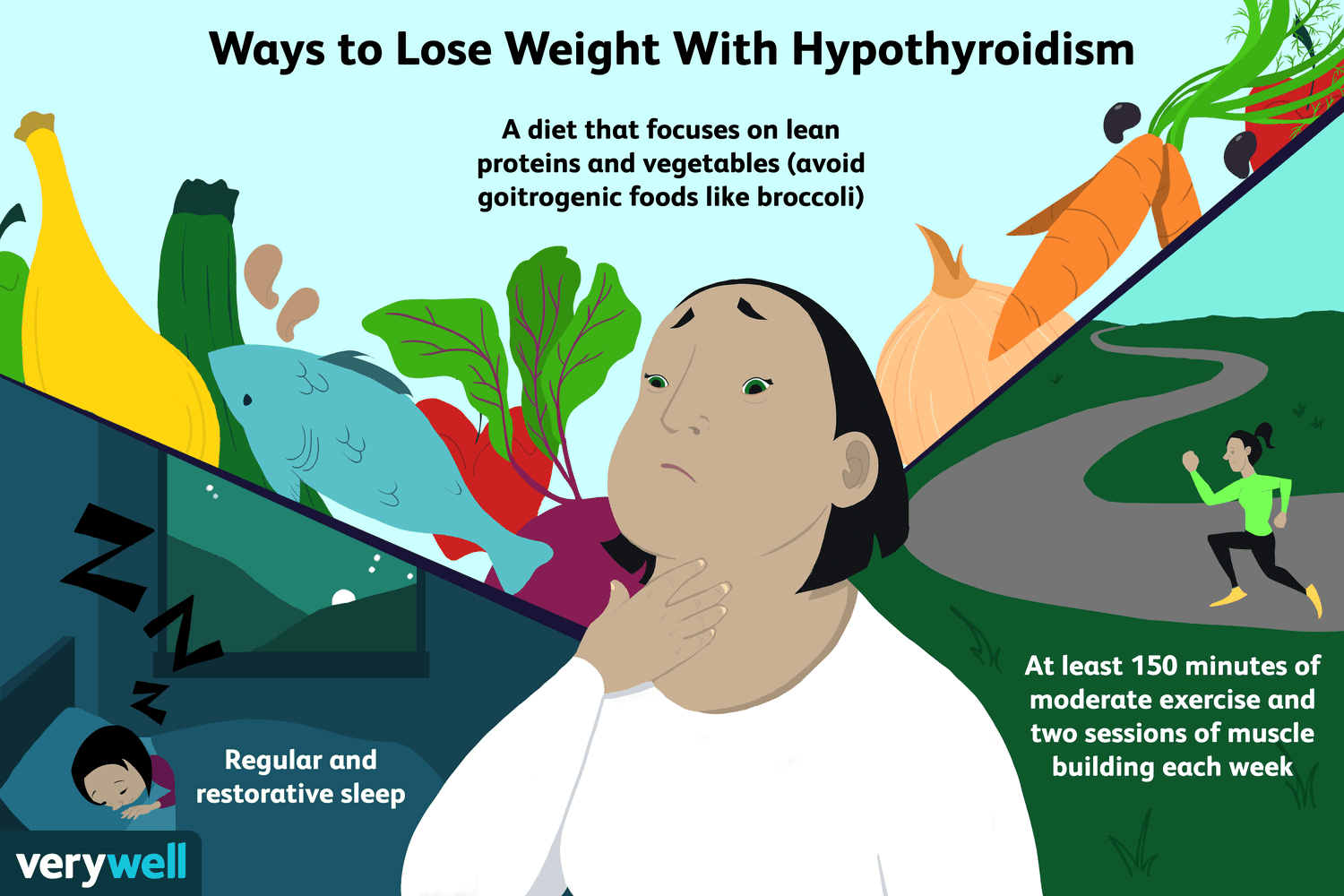
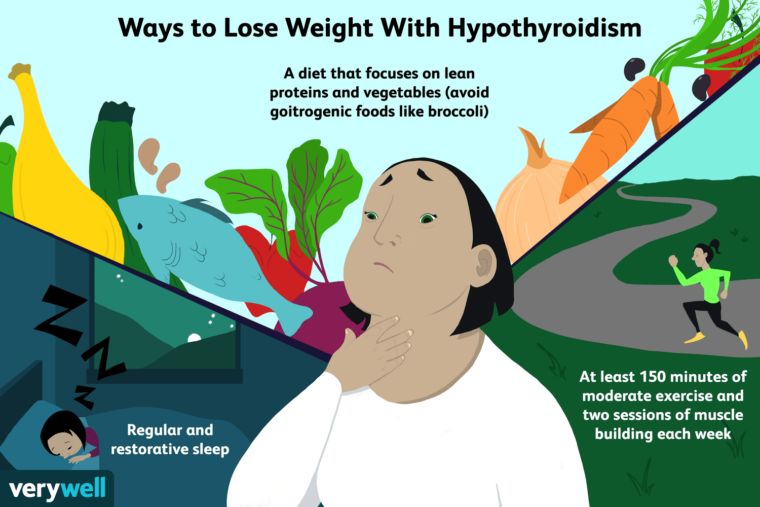
Effective Treatment Methods and Weight Management
Hypothyroidism can be managed with accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Common treatment methods include:
- Thyroid Hormone Replacement Therapy: Taking thyroid hormones to compensate for the deficiency.
- Lifestyle Improvements: Maintaining regular meals, sufficient sleep, and healthy lifestyle habits.
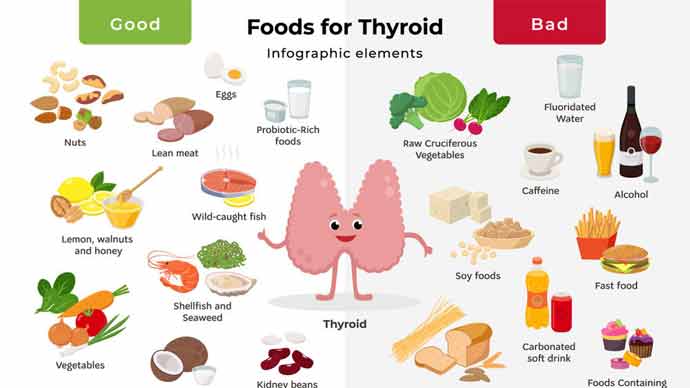
- Diet Control and Nutritional Management: Managing weight through proper diet control and nutritional management.
Importance of Diet Control and Nutritional Management
In hypothyroidism, diet control and nutritional management are crucial. To manage weight and alleviate various symptoms, consider the following:
- Healthy Eating Habits: Maintain regular meals and portion control.
- Nutrient Intake: Ensure adequate intake of nutrients, especially iron, zinc, and vitamin D.
Positive Impact Through Lifestyle Changes Improving
lifestyle habits is important for effectively managing hypothyroidism. Positive impacts can be achieved through the following changes:
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular exercise to stimulate metabolism.
- Sufficient Sleep: Get enough sleep to alleviate fatigue and lethargy.
- Stress Management: Find appropriate stress management methods, as stress can worsen hypothyroidism symptoms.
Long-term Health Management Plans for Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism requires long-term health management. The following plans can help manage hypothyroidism long-term:
- Regular Check-ups: Regularly undergo thyroid function tests and blood tests.
- Continuous Medication: Consistently take medication as prescribed by your doctor.
- Maintaining Healthy Lifestyle Habits: Maintain a healthy diet, regular exercise, and sufficient sleep.



Leave a Reply