Today, we’ll be exploring atopic dermatitis, a skin condition that concerns many. We’ll cover everything from its causes and symptoms to treatment options. I hope this information proves helpful to those interested in skin health!
Understanding Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic skin condition caused by inflammation. It typically arises from a combination of genetic factors and environmental triggers and is known to be challenging to prevent. Although it is commonly seen in children, adults can also be affected.
Exploring the Causes: Internal and External
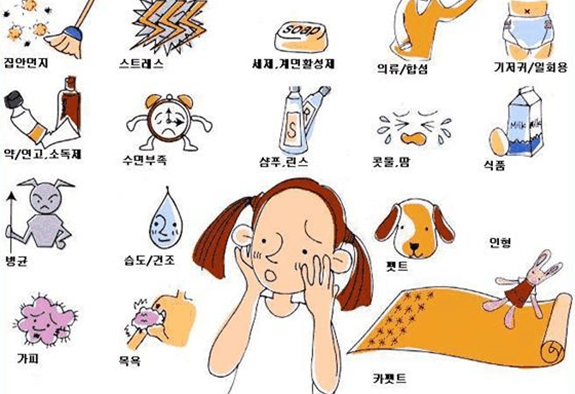
Factors The onset of atopic dermatitis is influenced by various internal and external factors. Genetics play a crucial role, with a family history increasing the likelihood of developing the condition. Environmental factors such as allergens, air pollution, humidity, and dry climates also contribute.
Identifying Key Symptoms and Signs
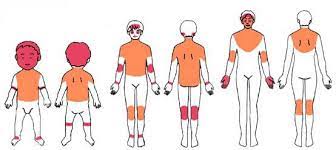
Symptoms of atopic dermatitis include rashes, itching, dryness, and sometimes fever. The most common manifestation is a rash accompanied by itching, typically occurring on the arms, legs, face, and neck. In severe cases, the skin may crack or become inflamed.
The Diagnostic Process
Diagnosing atopic dermatitis requires consultation with a dermatologist and skin testing. The diagnosis is made based on the patient’s symptoms, family history, and skin condition. Allergy tests may also be conducted to identify allergens.
Introduction to Common Treatment
Approaches Treatment for atopic dermatitis varies and may include medication, lifestyle adjustments, skin moisturizing, and managing home and environmental factors. These approaches should be tailored to the individual’s symptoms and condition.
Medication Treatment: Key Drugs Used
Treatments may involve antihistamines, steroid creams, and immunosuppressants. Each medication serves a specific purpose, with the prescription depending on the severity of symptoms and the individual’s condition.
Lifestyle Adjustments and Self-Care
Measures Managing atopic dermatitis also involves lifestyle adjustments and self-care. Important considerations include stress management, choice of clothing and detergents, and diet. Regular skin moisturization is also a crucial self-care measure.
The Importance of Skin Moisturization and Proper
Methods Due to the severe dryness associated with atopic dermatitis, moisturizing the skin is vital. Proper moisturization can be achieved through cool baths, lukewarm showers, and moisturizing creams. Choosing cosmetics with moisturizing ingredients is also beneficial.
Strategies for Managing Home and Environment
Preventing and managing atopic dermatitis involves proper home and environmental management. Removing dust and allergens during cleaning and using air purifiers can help. Maintaining a comfortable living environment by controlling humidity and temperature is also important.
Looking into Long-term Management and Prevention
Atopic dermatitis requires long-term management and preventive measures. Regular consultations and skin checks with a doctor are essential, and treatment should not be halted even if symptoms improve. Avoiding allergens and continuously moisturizing the skin are key preventive measures.
We’ve explored the basic understanding of atopic dermatitis, its causes, symptoms, diagnostic process, treatment approaches, lifestyle adjustments, medication, home, and environmental management strategies, and long-term management and prevention. Since treatment may vary based on individual symptoms and conditions, consulting with a doctor to find the most suitable treatment is crucial.
There are several foods that can help alleviate atopic dermatitis. These foods generally help reduce inflammation, strengthen the immune system, and improve skin health. Below are some foods known to be beneficial for atopic dermatitis:
- Foods rich in Omega-3 fatty acids: Omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce inflammation. Foods high in these fats include fatty fish like salmon and tuna, as well as flaxseeds and walnuts.
- Foods containing probiotics: These can help maintain a healthy gut environment and strengthen the immune system. Good sources include yogurt, kimchi, kefir, and sauerkraut.
- Foods rich in antioxidants: Fruits and vegetables are rich in antioxidants, which can help improve skin health. Berries, spinach, broccoli, and carrots are excellent choices.
- Foods high in Vitamin D: Vitamin D plays an important role in skin health and boosting the immune system. Foods rich in Vitamin D include salmon, sardines, and Vitamin D-fortified milk or orange juice.
- Foods high in Zinc: Zinc is important for skin healing. Pumpkin seeds, cashews, meat, and legumes are good sources of zinc.
In addition to consuming foods that may help with atopic dermatitis, it’s also beneficial to avoid foods that could trigger allergies. For instance, some people may react to gluten, dairy, nuts, soy, and eggs. These foods can potentially worsen atopic dermatitis, so considering their exclusion from your diet might be helpful. However, it’s important to remember that individual responses can vary, so consulting with a professional is advisable.





Leave a Reply