Understanding Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
Today, I want to talk about diabetes, a topic of interest to many people. We’ll explore the impact of diabetes on our bodies, its causes, and how it can be managed. I hope this discussion on diabetes will be helpful in some way. Let’s learn together!

Understanding Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
- Basic Understanding of Diabetes: Definition and Importance
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by the inability to effectively regulate glucose (blood sugar) in the blood. It can result from a lack of insulin or insulin dysfunction. Diabetes is a global health issue, and early detection and proper management are crucial.

- Causes of Diabetes: Differences Between Types
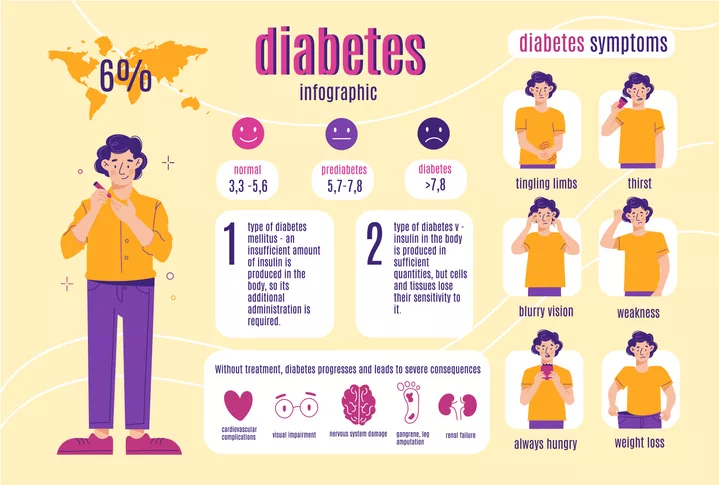
Diabetes is categorized into Type 1 and Type 2. Type 1 diabetes occurs when autoimmune processes destroy insulin-producing beta cells. On the other hand, Type 2 diabetes can result from obesity, genetic factors, lifestyle habits, etc. Gestational diabetes, which develops during pregnancy, also deserves attention.

- Major Symptoms and Identification Methods of Diabetes
Early symptoms of diabetes include frequent urination, thirst, increased appetite, and weight loss. Since these symptoms can also relate to other conditions, blood sugar measurements and related tests are necessary for an accurate diagnosis.
- Diabetes Diagnosis: Required Tests and Procedures
Diagnosing diabetes requires fasting blood sugar tests, oral glucose tolerance tests, and glycated hemoglobin (A1C) tests. These tests help in accurately diagnosing diabetes and determining its type.

- Importance of Blood Sugar Control and Basic Knowledge
Blood sugar control is central to diabetes management. It’s important to regulate various factors, including diet, exercise, and medication, to maintain stable blood sugar levels. Keeping fasting blood glucose and A1C levels within the normal range is crucial.
- Dietary Management and the Role of Nutritional Components
Dietary management is vital for people with diabetes. Consuming low GI foods, high-fiber foods, and healthy fats can aid in blood sugar control. Additionally, the proportion and intake of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats need to be adjusted appropriately.

- Exercise and Diabetes Management: Practical Guide
Exercise plays a crucial role in managing diabetes. Combining aerobic and strength training exercises can help control blood sugar and manage weight. It’s also important to monitor blood sugar levels before and after exercise and to be aware of precautions.
- Medication Treatment and Insulin Usage
Many people with diabetes need medication to control their blood sugar. Proper use of oral medications and insulin injections is important for stabilizing blood sugar. Understanding medication dosages and precautions is essential.

- Managing Diabetes Through Lifestyle Changes
Diabetes is significantly influenced by lifestyle habits. Adopting healthy lifestyle habits, such as quitting smoking, moderating alcohol consumption, and managing stress, can prevent the onset and progression of diabetes. Regular health check-ups and consistent consultation with a doctor are also necessary.
- Long-term Perspective on Diabetes Prevention and Management Strategies
Diabetes is a chronic condition that requires long-term prevention and management. Healthy eating habits, regular exercise, and routine check-ups can prevent the development of diabetes and its complications.
Here’s the translation:
Early symptoms of diabetes:
Frequent urination, thirst, increased appetite, weight loss, etc.
Foods good for diabetes:
High fiber foods, low GI foods, healthy fats, etc. should be consumed.
Normal diabetes values:
Fasting blood sugar 70-100 mg/dL, glycated hemoglobin below 5%.
Diabetes tests:
Fasting blood sugar measurement, oral glucose tolerance test, glycated hemoglobin test, etc.
Type 2 diabetes:
Caused by obesity, genetic factors, lifestyle habits, etc.
Type 1 diabetes:
Occurs when beta cells are destroyed by an autoimmune response.
Diabetic food:
Low GI fruits, vegetables, high protein low fat foods, etc.
Diabetes tests:
Diagnosed through fasting blood sugar measurement, glycated hemoglobin test, oral glucose tolerance test, etc.
Diabetes surgery:
Surgical option exists for treating diabetes in obese patients.
Endocrinology:
Specializes in the diagnosis and management of diabetes.
Diabetes occurrence:
Caused by obesity, genetic factors, lifestyle habits, etc.
Type 1 diabetes:
Another name for Type 1 diabetes.
Diabetes values:
Maintain fasting blood sugar 70-100 mg/dL, glycated hemoglobin below 5%.
Diabetes tests:
Various tests such as blood tests, urine tests, neurological tests, etc., are conducted.
Diabetes surgery:
Surgical option is available for treating diabetes in obese patients.
Diabetes onset:
Caused by obesity, genetic factors, lifestyle habits, etc.
Through this comprehensive exploration, we’ve learned about understanding and managing diabetes effectively. Early detection and proper management can prevent the onset of complications. A healthy lifestyle, consistent consultation with a doctor, and proper adjustment of diet, exercise, and medication are essential for effectively managing diabetes. 🩺🧡