Degenerative Arthritis
A to Z: Understanding Degenerative Arthritis from Prevention to Treatment
Hello! With the weather being unpredictable lately, many of you might be feeling discomfort in your joints. In this post, we will explore degenerative arthritis from A to Z. Let’s learn about prevention methods and treatment options together! Let’s share healthy information and create a better daily life!

What is Degenerative Arthritis?
Degenerative arthritis is a condition that occurs as the cartilage in the joints gradually deteriorates. While it primarily affects older individuals, it can also be accelerated by factors such as obesity, lack of exercise, and trauma. This condition commonly manifests in the knees, hips, and finger joints. Degenerative arthritis can cause joint pain and inflammation, hindering daily activities, and in severe cases, can make movement difficult. Early detection and appropriate management are crucial, and improving personal lifestyle habits can contribute to prevention and treatment.
Major Causes of Degenerative Arthritis
The primary causes of degenerative arthritis include natural age-related changes as well as various other factors. Obesity increases pressure on the joints, accelerating damage, and genetic predisposition can raise the likelihood of developing the condition. Additionally, repetitive joint use, trauma, and certain occupational activities contribute to the onset of this disease. These various causes work in tandem to damage the cartilage in the joints, leading to inflammation and pain.
Understanding Symptoms and Early Signs
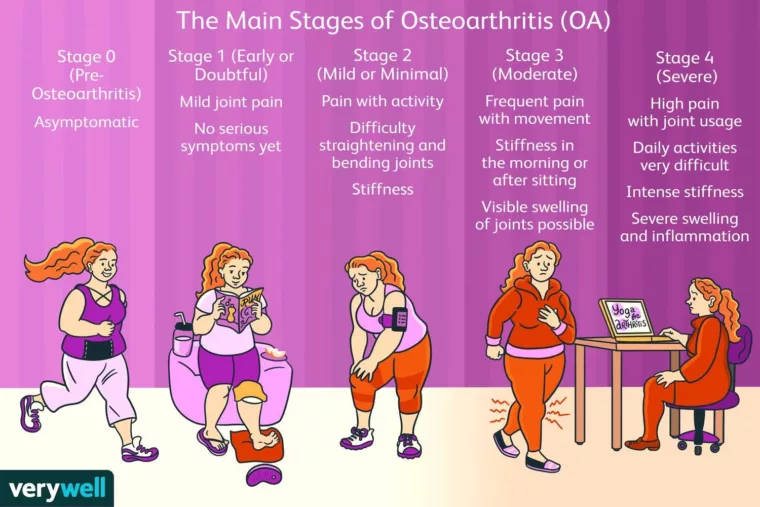
The initial signs of degenerative arthritis start with mild pain or discomfort. Common symptoms include stiffness in the joints upon waking in the morning, fatigue after activity, and pain during specific movements. It is particularly important to pay attention when the joints swell or feel uncomfortable. If symptoms are not recognized and managed appropriately in the early stages, the condition can progressively worsen, significantly lowering the quality of life. Therefore, being sensitive to early symptoms is vital.
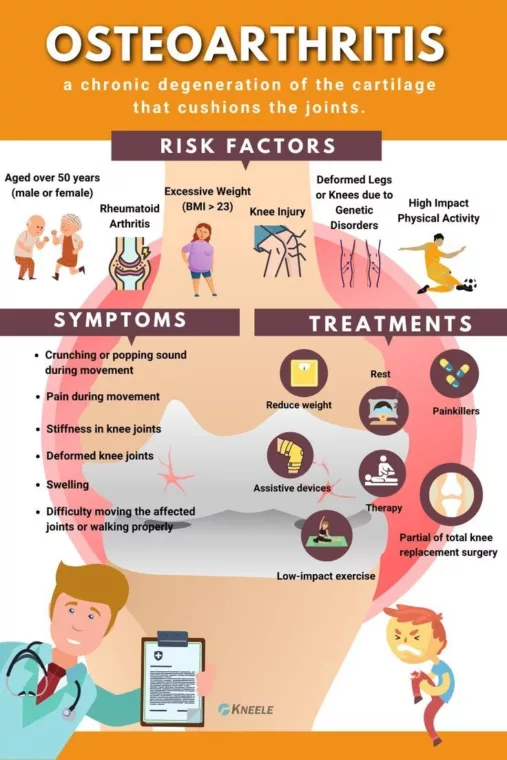
The Importance of Diagnosis and Testing
Diagnosing degenerative arthritis involves a physical examination and medical history review by a physician. Initially, a simple assessment of joint movement and pain levels is conducted, and imaging tests such as X-rays or MRIs may be performed to get a more precise view of the joint condition if necessary. Diagnostic tests are essential for establishing an accurate treatment plan, and the earlier the diagnosis, the more effective the treatment can be. Regular check-ups are important for proper management and treatment.
Lifestyle Habits for Prevention
Maintaining healthy lifestyle habits is essential for preventing degenerative arthritis. Regular exercise can strengthen the joints and help control weight, thus reducing the burden on the joints. Low-impact aerobic exercises and strength training are recommended, along with stretching and flexibility exercises. Maintaining a proper diet and using assistive devices when necessary can also help protect joint health. These preventive measures can enhance quality of life and reduce the risk of developing degenerative arthritis.

Treatment Options and Latest Technologies
The treatment of degenerative arthritis aims to alleviate symptoms and slow disease progression. Initially, non-drug treatments such as physical therapy and various exercise therapies are implemented to relieve pain and restore function. If medication is needed, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may be used, or injections for pain control might be administered. The latest technologies include gene therapy methods like stem cell treatment, which show potential for repairing and regenerating damaged cartilage. A combination of various treatment options can provide personalized management.
The Role of Diet and Nutritional Management
Diet and nutritional management play significant roles in the prevention and treatment of degenerative arthritis. It is recommended to consume foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fish, along with plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables. Foods high in vitamin D and calcium are particularly beneficial for bone health. Limiting processed foods and sugar while maintaining a balanced diet can help reduce the burden on the joints and alleviate inflammation. A combination of nutrients and proper intake also supports overall health maintenance.
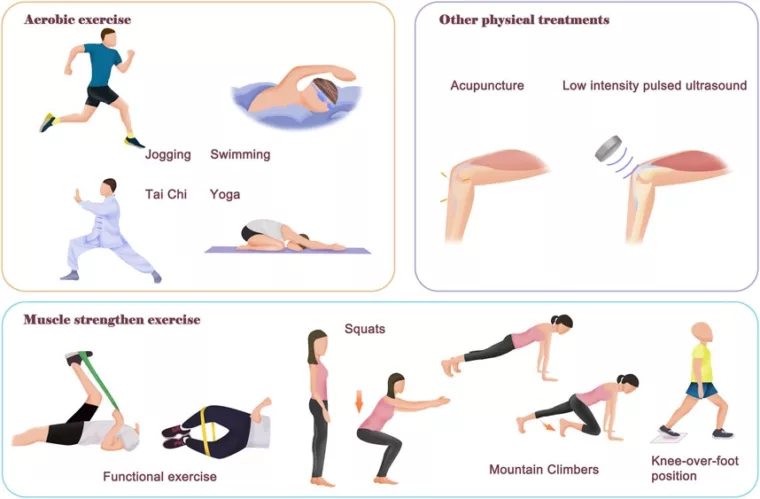
Benefits of Physical Therapy and Exercise
Physical therapy and exercise are essential elements in managing degenerative arthritis. Physical therapists design personalized programs to restore joint function, increase flexibility, and strengthen the joints. Exercise helps strengthen the muscles around the joints and improve stability, reducing pain. It’s advisable to start with low-impact exercises and gradually increase the intensity. This approach helps manage joint pain and improves mobility in daily life, enhancing quality of life.