Complex but Understandable Alopecia Areata: Causes and Treatments
Today, I’d like to talk to you about alopecia areata. It’s a somewhat complex form of hair loss, but by understanding its causes and treatments, it becomes comprehensible!

Understanding Alopecia Areata: Definition and Overview
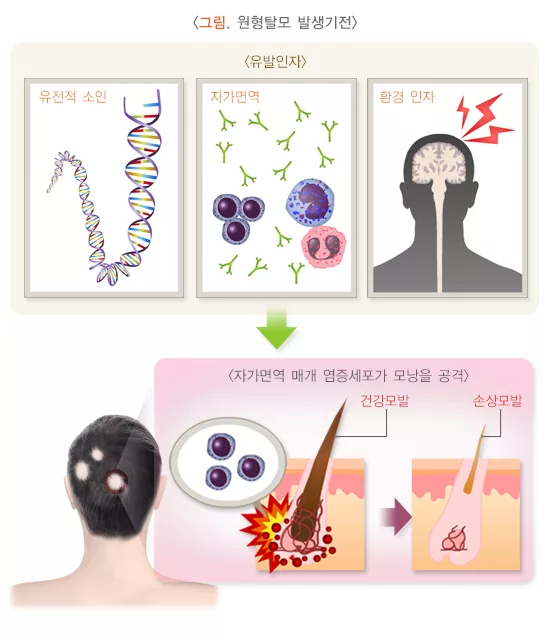
Alopecia areata refers to a condition where hair falls out in identifiable circular patterns. It’s most commonly seen among men but can also occur in women. Typically, genetic factors are known to be the main cause, with other elements like hormonal changes, aging, and stress also playing a role in the onset and progression of the condition.
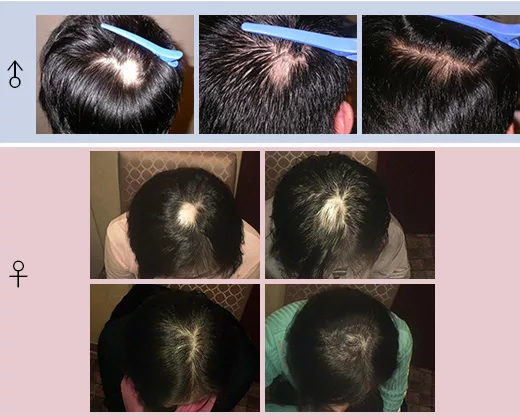
Exploring the Main Causes of Alopecia Areata
One of the primary causes of alopecia areata is genetic factors. If there’s a family history, the likelihood of developing alopecia areata increases. Hormonal changes are also known to cause this type of hair loss, especially when levels of testosterone, a male hormone, exceed normal levels and interfere with hair growth. Additionally, stress, aging, and environmental factors can influence the development and progression of alopecia areata.
Identifying Initial Signs and Symptoms
The early signs of alopecia areata can vary. In most cases, the first symptom is the gradual thinning and shedding of hair, particularly on the crown of the head. You might also notice a decrease in hair density and more visible scalp. Identifying these early signs and addressing them promptly is crucial.
Tests and Procedures for Accurate Diagnosis
To accurately diagnose alopecia areata, it’s important to differentiate it from scarring alopecia and other forms of hair loss. Dermatologists will conduct a thorough examination of the patient’s medical history and symptoms, along with physical exams, blood tests, and tissue biopsies. Scalp scaling and trichoscopy can also aid in the diagnosis.
Various Treatment Options for Alopecia Areata
The treatment approaches for alopecia areata vary and are chosen based on the individual patient’s condition. Common treatments include medication, non-medical methods, and hair transplantation. Medications typically involve the use of anti-inflammatory drugs or anti-androgens to stimulate hair growth and prevent further loss. Non-medical methods include scalp massages, scalp care products, and natural remedies. In severe cases, hair transplantation may be considered.
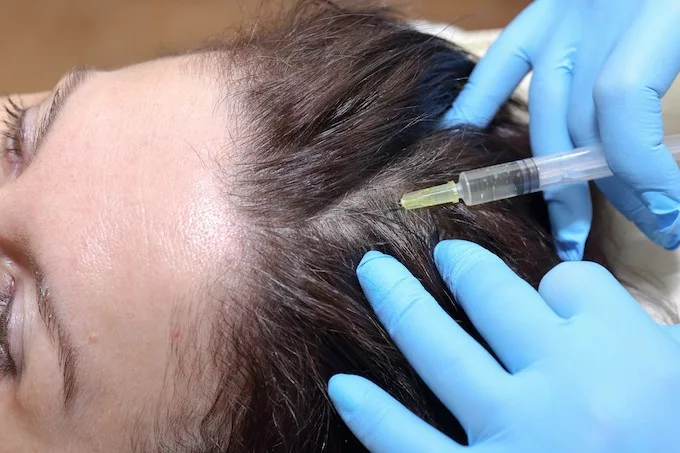
Medication Treatments and Their Effectiveness
Medication is one of the most common treatment methods for alopecia areata, with minoxidil and finasteride being the most widely used drugs. These medications help stimulate hair growth and prevent hair loss. However, the effectiveness of these treatments can vary from person to person and requires continuous use. Side effects should also be monitored closely.
Non-Medical Treatment Methods and Natural Remedies
Non-medical treatments for alopecia areata come in various forms. Scalp massages can promote blood circulation to the scalp and aid in hair growth. Maintaining a healthy scalp with the right care products is also crucial. Natural remedies may include homemade scalp masks and medicinal plant extracts to nourish the hair and prevent hair loss.
Managing Hair Loss Through Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes play a significant role in managing alopecia areata. Maintaining a healthy diet and balanced nutrient intake can benefit hair health. Managing stress, ensuring adequate rest, and engaging in regular exercise are also important for preventing hair loss and aiding in fatigue recovery.
Preventing Recurrence and Long-Term Management Strategies
Even after successful treatment of alopecia areata, continuous management is necessary to prevent recurrence. Regular visits to the clinic and following the advice of a specialist for ongoing medication or non-medical treatments are essential. Improving lifestyle habits and managing stress can also contribute to long-term hair loss management.
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder that occurs when the immune system attacks hair follicles. While it cannot be definitively said that specific foods directly cure alopecia areata, consuming foods that support healthy hair growth and strengthen the immune system is beneficial.

Here are some foods that may help with alopecia areata:
- Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids: Foods such as salmon, tuna, flaxseed, and walnuts, which are high in omega-3 fatty acids, can reduce inflammation and promote hair growth.
- Foods high in vitamin E: Almonds, spinach, and sunflower seeds, which are rich in vitamin E, can improve blood circulation and support the health of hair follicles.
- Iron-rich foods: Consume foods rich in iron, which helps in the formation of red blood cells and the delivery of oxygen to hair follicles. Iron can be found in spinach, lentils, and beef.
- Foods high in zinc: Pumpkin seeds, cashews, and beef are rich in zinc, a mineral that plays an important role in hair growth. A lack of zinc can lead to hair loss.
- Biotin-rich foods: Eggs, avocado, and legumes, which are rich in biotin, play a crucial role in hair growth.
In addition to these, maintaining a balanced diet for overall health, staying hydrated, and reducing the intake of processed and sugary foods is advisable. If necessary, consider consulting with a doctor to take appropriate health supplements if diet alone is insufficient.